Next: Generating Initial Data with Up: IDBrillData Previous: Abstract Contents
Purpose
The purpose of this thorn is to create (time symmetric) initial data
for a Brill wave spacetime. It does so by starting from a
three-metric of the form originally considered by Brill
Thorn IDBrillData provides three choices for the ![]() function:
an exponential form, (IDBrillData::q_function = "exp")
function:
an exponential form, (IDBrillData::q_function = "exp")
![\begin{displaymath}
q = a \; \frac{\rho^{2+b}}{r^2} e^{-\left( \frac{z}{\sigma_z...
...m}{1 + e \rho^m}
\cos^2 \left( n \phi + \phi_0 \right) \right]
\end{displaymath}](img486.png) |
(part342) |
![\begin{displaymath}
q = a \left( \frac{\rho}{\sigma_\rho} \right)^b \frac{1}{1 +...
...m}{1 + e \rho^m}
\cos^2 \left( n \phi + \phi_0 \right) \right]
\end{displaymath}](img487.png) |
(part343) |
![\begin{displaymath}
q = a \left( \frac{\rho}{\sigma_\rho} \right)^b e^{-\left[
\...
...m}{1 + e \rho^m}
\cos^2 \left( n \phi + \phi_0 \right) \right]
\end{displaymath}](img488.png) |
(part344) |
Substituting the metric into the Hamiltonian constraint gives an
elliptic equation for the conformal factor ![]() which is then
numerically solved for a given function
which is then
numerically solved for a given function ![]() :
:
| (part345) |
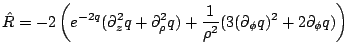 |
(part346) |
Assuming the initial data to be time symmetric means that the momentum constraints are trivially satisfied.
In the case of axisymmetry (that is ![]() in the above expressions for
in the above expressions for
![]() ), the Hamiltonian constraint can be written as an elliptic
equation for
), the Hamiltonian constraint can be written as an elliptic
equation for ![]() with just the flat space Laplacian,
with just the flat space Laplacian,
| (part347) |
Next: Generating Initial Data with Up: IDBrillData Previous: Abstract Contents