Next: High-level Reduction Operations Up: Reduction Operations Previous: Reduction Operations Contents
Basic Reduction Operations
The following reduction operations are imlemented.- count:
- The number of values
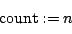
- sum:
- The sum of the values
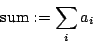
- product:
- The product of the values
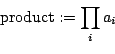
- sum2:
- The sum of the squares of the values
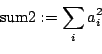
- sumabs:
- The sum of the absolute values
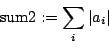
- sumabs2:
- The sum of the squares of the absolute values
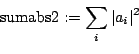
- min:
- The minimum of the values
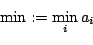
- max:
- The maximum of the values
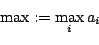
- maxabs:
- The maximum of the absolute values
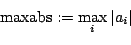
and define the maximum equivalently.
Next: High-level Reduction Operations Up: Reduction Operations Previous: Reduction Operations Contents