Next: Checkpointing & Recovery Up: IOFlexIO Previous: Serial versus Parallel Output Contents
Output of Hyperslab Data
By default, thorn IOFlexIO outputs multidimensional Cactus variables with their full contents resulting in maximum data output. This can be changed for individual variables by specifying a hyperslab as a subset of the data within the N-dimensional volume. Such a subset (called a hyperslab) is generally defined as an orthogonal region into the multidimensional dataset, with an origin (lower left corner of the hyperslab), direction vectors (defining the number of hyperslab dimensions and spanning the hyperslab within the N-dimensional grid), an extent (the length of the hyperslab in each of its dimensions), and an optional downsampling factor.
Hyperslab parameters can be set for individual variables using an option string appended to the variables' full names in the IOFlexIO::out_vars parameter.
Here is an example which outputs two 3D grid functions Grid::r and Wavetoy::phi. While the first is output with their full contents at every 5th iteration (overriding the IOFlexIO::out_every parameter for this variable), a two-dimensional hyperslab is defined for the second grid function. This hyperslab defines a subvolume to output, starting with a 5 grid points offset into the grid, spanning in the yz-plane, with an extent of 10 and 20 grid points in y- and z-direction respectively. For this hyperslab, only every other grid point will be output.
IOFlexIO::out_every = 1
IOFlexIO::out_vars = "Grid::x{ out_every = 5 }
Wavetoy::phi{ origin = {4 4 4}
direction = {0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1}
extent = {10 20}
downsample = {2 2} }"
The hyperslab parameters which can be set in an option string are:
- origin
This specifies the origin of the hyperslab. It must be given as an array of integer values with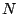 elements. Each value specifies the offset in
grid points in this dimension into the N-dimensional volume of the grid
variable.
elements. Each value specifies the offset in
grid points in this dimension into the N-dimensional volume of the grid
variable.
If the origin for a hyperslab is not given, if will default to 0. - direction
The direction vectors specify both the directions in which the hyperslab should be spanned (each vector defines one direction of the hyperslab) and its dimensionality (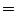 the total number of dimension vectors).
The direction vectors must be given as a concatenated array of integer
values. The direction vectors must not be a linear combination of each other
or null vectors.
the total number of dimension vectors).
The direction vectors must be given as a concatenated array of integer
values. The direction vectors must not be a linear combination of each other
or null vectors.
If the direction vectors for a hyperslab are not given, the hyperslab dimensions will default to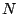 , and its directions are parallel to the
underlying grid.
, and its directions are parallel to the
underlying grid.
- extent
This specifies the extent of the hyperslab in each of its dimensions as a number of grid points. It must be given as an array of integer values with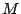 elements (
elements (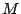 being the number of hyperslab dimensions).
being the number of hyperslab dimensions).
If the extent for a hyperslab is not given, it will default to the grid variable's extent. Note that if the origin is set to a non-zero value, you should also set the hyperslab extent otherwise the default extent would possibly exceed the variable's grid extent. - downsample
To select only every so many grid points from the hyperslab you can set the downsample option. It must be given as an array of integer values with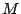 elements (
elements (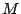 being the number of hyperslab dimensions).
being the number of hyperslab dimensions).
If the downsample option is not given, it will default to the settings of the general downsampling parameters IO::out_downsample_[xyz] as defined by thorn IOUtil.
Next: Checkpointing & Recovery Up: IOFlexIO Previous: Serial versus Parallel Output Contents