Next: Extracting/distributing a hyperslab Up: CCTK Hyperslab API Specification Previous: CCTK Hyperslab API Specification Contents
Defining a hyperslab mapping
An ![]() -dimensional hyperslab subspace mapped into an
-dimensional hyperslab subspace mapped into an ![]() -dimensional space
can be specified either by coordinates on the physical grid or by index
points on the underlying computational grid.
-dimensional space
can be specified either by coordinates on the physical grid or by index
points on the underlying computational grid.
CCTK_INT Hyperslab_GlobalMappingByIndex (
CCTK_POINTER_TO_CONST GH,
CCTK_INT vindex,
CCTK_INT hdim,
const CCTK_INT *direction /* vdim*hdim */,
const CCTK_INT *origin /* vdim */,
const CCTK_INT *extent /* hdim */,
const CCTK_INT *downsample /* hdim */,
CCTK_INT table_handle,
CCTK_FPOINTER conversion_fn,
CCTK_INT *hsize /* hdim */);
CCTK_INT Hyperslab_GlobalMappingByPhys (
CCTK_POINTER_TO_CONST GH,
CCTK_INT vindex,
CCTK_INT hdim,
CCTK_STRING coord_system_name,
const CCTK_INT *direction /* vdim*hdim */,
const CCTK_REAL *origin /* vdim */,
const CCTK_REAL *extent /* hdim */,
const CCTK_INT *downsample /* hdim */,
CCTK_INT table_handle,
CCTK_FPOINTER conversion_fn,
CCTK_INT *hsize /* hdim */);
CCTK_INT Hyperslab_LocalMappingByIndex (
CCTK_POINTER_TO_CONST GH,
CCTK_INT vindex,
CCTK_INT hdim,
const CCTK_INT *direction /* vdim*hdim */,
const CCTK_INT *origin /* vdim */,
const CCTK_INT *extent /* hdim */,
const CCTK_INT *downsample /* hdim */,
CCTK_INT table_handle,
CCTK_FPOINTER conversion_fn,
CCTK_INT *hsize_local, /* hdim */
CCTK_INT *hsize_global, /* hdim */
CCTK_INT *hoffset_global /* hdim */);
CTK_INT Hyperslab_LocalMappingByPhys (
CCTK_POINTER_TO_CONST GH,
CCTK_INT vindex,
CCTK_INT hdim,
CCTK_STRING coord_system_name,
const CCTK_INT *direction /* vdim*hdim */,
const CCTK_REAL *origin /* vdim */,
const CCTK_REAL *extent /* hdim */,
const CCTK_INT *downsample /* hdim */,
CCTK_INT table_handle,
CCTK_FPOINTER conversion_fn,
CCTK_INT *hsize_local, /* hdim */
CCTK_INT *hsize_global, /* hdim */
CCTK_INT *hoffset_global /* hdim */);
Function arguments:
- CCTK_POINTER_TO_CONST GH
The reference to the CCTK grid hierarchy.In a C implementation, this should be a pointer of type const cGH *.
- CCTK_INT vindex
In order to compute a hyperslab mapping, a CCTK grid variable must be given by this argument which will be used as a template in the following hyperslab get/put operation to denote the input arrays' domain decomposition (dimensionality and distribution over processors). The domain decomposition of all input CCTK variables given by the vindex, vindices arguments in subsequent calls to Hyperslab_GetXXX()/Hyperslab_PutXXX() must match the one of the template variable vindex. - CCTK_INT hdim
The dimension of the hyperslab to get/put (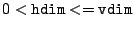 ).
).
- const CCTK_INT *direction
const CCTK_INT *origin
const CCTK_INT *extent
const CCTK_INT *downsample
-------------
const CCTK_CHAR *coord_system_name
const CCTK_INT *direction
const CCTK_REAL *origin
const CCTK_REAL *extent
const CCTK_INT *downsample
Arguments describing the actual mapping of the hyperslab to get/put.The hyperslab location is identified by its origin (lower left corner), the direction vectors starting from the origin and spanning the hyperslab in the
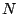 -dimensional space, and its extents (size of the hyperslab in
each direction).
-dimensional space, and its extents (size of the hyperslab in
each direction).
There are hdim direction vectors (one for each hyperslab axis) with vdim elements. The direction vectors are given in grid index points and must be linearly independent. The direction argument must be passed as an array direction[vdim_index + hdim_index*vdim] (vdim is the fastest changing dimension).
The origin and extent can be given in either physical coordinates or grid points - for the first case a coordinate system needs to be given to do the mapping onto the underlying grid. For the second case, integer extents can be given as negative values meaning that the hyperslab mapping should be defined with the maximum possible extents (ie. the size of the underlying grid).
The downsampling parameter denotes the downsampling factors for the hyperslab to be extracted/distributed. They are given in terms of grid points in each hyperslab direction. The downsampling parameter is optional - if NULL is passed here, no downsampling will be applied.
- CCTK_INT table_handle
A key/value table can be passed in via its handle to provide additional information to the hyperslab get/put routines about the hyperslab mapping. For example, there could be a tolerance parameter for hyperslabs which are not rectangular to the underlying grid. For grid points which offset from the direction vectors, the tolerance would then specify a (plus/minus) offset for the directions saying which points should still be included in the hyperslab space.Another example could be whether to do interpolation between grid points or not.
Passing a table handle is optional, an invalid (negative) table handle denotes no additional table information.
- CCTK_FPOINTER conversion_fn
Reference to a user-defined datatype conversion function.Users can request a type conversion between input and output data during a hyperslab get/put operation. A hyperslab API implementation may provide a set of predefined data type conversion routines for this purpose. In addition to this feature, users can also provide their own data type conversion function and pass a reference to it in the conversion_fn argument.
For a C implementation, such a user-supplied conversion function should be declared according to the following typedef:
typedef CCTK_INT (*t_hslabConversionFn) (CCTK_INT nelems, CCTK_INT src_stride, CCTK_INT dst_stride, CCTK_INT src_type, CCTK_INT dst_type, CCTK_POINTER_TO_CONST src, CCTK_POINTER dst);A data type conversion function gets passed the number of elements to convert (nelems), the strides between adjacent elements in the source and destination arrays (src_stride, dst_stride), the source and destination CCTK datatypes (src_type, dst_type), a pointer to the data to convert (src), and a pointer to the conversion target buffer (dst). The routine should return the number of elements converted (nelems) for success.
If a user-supplied function is given (conversion_fn is not NULL), subsequent hyperslab get/put calls will use for data type conversions. Otherwise the hyperslab get/put calls should fall back to using an appropriate predefined data conversion function (if any exists).
- CCTK_INT *hsize
CCTK_INT *hsize_local
Reference to a size array with hdim elements to be set by the Hyperslab_XXXMappingByXXX() routines.The resulting size of the hyperslab to be extracted is set according to the hyperslab extents and downsampling parameters chosen. With this information, one can compute the overall size of the hyperslab, allocate memory for it and pass it as a user-provided hyperslab data buffer into subsequent calls to Hyperslab_GetXXX().
- CCTK_INT *hsize_global
Reference to a size array with hdim elements to be set by the Hyperslab_LocalMappingBy*() routine.This array holds the sizes of the corresponding global hyperslab. It is set according to the local hyperslab extents and downsampling parameters chosen and locates the local hyperslab in the global grid.
A value of NULL can be passed for hsize_global if no information about the global hyperslab size is needed.
- CCTK_INT *hoffset_global
Reference to an offset array with hdim elements to be set by the Hyperslab_LocalMappingBy*() routine.This array holds the offsets of the local hyperslab into the corresponding global hyperslab. It is set according to the local hyperslab extents and downsampling parameters chosen and locates the local hyperslab in the global grid.
A value of NULL can be passed for hoffset_global if no information about a hyperslab offsets is needed.
Return codes (according to the Cactus Coding Conventions):
- 0 for success
- negative for some error condition (to be defined by an actual implementation of the Hyperslab_*MappingBy*() routines)
Next: Extracting/distributing a hyperslab Up: CCTK Hyperslab API Specification Previous: CCTK Hyperslab API Specification Contents